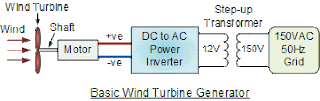
It is possible to use a 12V DC motor (I assume its a car starter motor) as a wind turbine generator to provide energy conversion between the mechanical torque from the wind rotor turbines, (called the prime mover) and the connected 150V load. A gearless two or three bladed upwind wind turbine using a permanent magnet DC motor can be used to charge a battery for energy storage through a rectifier and a typical wind turbine configuration is given as:
However, using a low voltage DC motor as a wind turbine generator is not always a good idea for the following reasons.
- The DC motor may not be rated for continuous use and overheat.
- The motors maximum rotational speed may be exceeded on a gusty day resulting in bearing or mechanical failure of the armature, slip-rings and brushes.
- A DC motor used as a generator does not provide a constant output voltage, when the shaft speed and the load current vary.
- The output current may be high at a low 12V DC voltage requiring large diameter, low resistance cables between the generator and batteries.
- The storage batteries and inverter electronics need to be as close as possible to the generator to reduce power loss in the cables.
- The motors permanent magnets will attract ferromagnetic dust and debris.
- Also relating to your situation, a special centre tapped “step-up” transformer is required to convert the 12V to 150V.
- Then the alternative is to use a high voltage output wound rotor induction machine as a Wind Power Generator.
Regarding the electronics. You need to increase the voltage from 12 volts to 150 volts, therefore you will need a step-up transformer with a turns ratio of 1:12.5, The output power required on the secondary winding is: V x I = 150 x 1.5 = 225 VA minimum. Then the primary winding will be: 225 ÷ 12 = 18.75 amps. Therefore, you will require a transformer with a primary winding capable of handling 20 amps minimum as well as the switching transistors.
For a 50 or 60Hz output frequency the primary switching transistors (or Mosfets) need to switch at this frequency. A simple RC or RL oscillator can be constructed to produce the required sinusoidal waveform to convert the DC to an AC signal. It must have two complementary outputs “Q” and “not Q” to switch both halves of the transformer primary, You can use NAND gates or NOT gates (7400, 7404, 4069 etc) as an IC multivibrator but these will produce a square wave output signal.
The switching transistors can be any high current type capable of switching 20 amps at 40 volts minimum such as the 2N3771 or the TIP35C, or use lower current transistors in parallel but use a heatsink. Darlington transistors such as the NPN 2N6284 or the NPN SGSD100. One suggested (but not tested) switching circuit could be:
Possible Switching CircuitEach half of the transformer primary is switched in turn to produce the secondary output. Because of the high current flow in the primary windings large diameter cables must be used. The pilot switching transistors can be any small 5-6 amp NPN transistor such as the TIP41, TIP121 etc. The diode is a normal 1-2 amp power diode.




 Posted in:
Posted in: 





