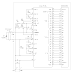
This simple but complete Theremin circuit is constructed using only two inverter chip plus one regulator IC. This Theremin circuit consist of five functional blocks: power supply regulator, hand controlled oscillator, null oscillator, mixer, and filter
The power supply regulator consist of LP2950 regulator IC, which stabilize the voltage from battery to 5V. You can use more popular 7805 IC for this, but since the power consumption of this Theremin circuit is very small, then you can use 78L05 which is smaller. CR1 diode is used to protect from inappropriate battery polarity, shorting the battery voltage together with R8 100 Ohm resistor which prevent the large current when the battery is installed in wrong direction. Although the inverter chip will work well for 9V battery, there is a benefit of using voltage regulation to regulate the battery voltage at lower voltage level, that the voltage will remain constant for until the end of battery life. This will avoid frequency drift of the Theremin’s null oscillator which should be carefully adjusted to zero the output frequency, which can be affected by the supply voltage.
Hand Controlled Oscillator
The hand proximity sensor is an oscillator which has antenna extension which shift the capacity coupling in the loop. This capacitance shift occur when we move our hand approaching the antenna. Since this change is very small in percentage, we need this oscillator to be high enough to produce notable frequency difference. This oscillator block is built around U1A, U1B, and U1C. This oscillator give oscillation at around 73kHz. This frequency is not directly audible, we have to process this signal further to produce audible signal.
Null Oscillator
Null oscillator is employed to produce a constant frequency oscillation that will be used to produce differential frequency which is audible. This oscillator block is built around U2A, U2B, and U2C. This null oscillator should be adjustable to set the null point where the Theremin should produce no oscillation at certain hand position. At this point, the null oscillator should be adjusted to have same frequency with the hand controlled oscillator since the audible Theremin output is the product of the difference between hand controlled and null oscillator frequencies.
Frequency Mixer (Differentiator)
The mixer is used to mix the signal from two oscillators, the hand controlled and the null oscillators. This mixer produce an output which contain many frequency components, not only the difference but also the original and the sum, since the amplifier U1F is basically a digital inverter which has non-linear transfer function. Fortunately, all the frequency components, except the difference, will be much higher than the needed signal and inaudible. This make it easy to remove by simple low pass filter to obtain only the differential frequency component.
Low Pass Filter
As stated before, we need to obtain only the audible frequency component by low-pass filtering. Although the high frequencies is inaudible, we still have to remove it since it can cause damage in audio power amplifier is the level is too high. It can distort the audible signal, and it can eat the electric power like ghost, frying your amplifier or at least make it overheated. This Theremin circuit use simple low pass filter consist of C4, R5, and R7 for the passive stage, and C2 inside the inverter amp loop.