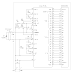
With the code set correctly, the NAND gate output will stay low and flip-flop can be toggled any number of times, making it possible to switch on or switch off the relay, as desired. Suppose we are using the system for switching-on of a deck for which the power supply is routed via the contacts of the relay. The authorised person would select correct code which would cause the supply to become available to the deck. After use he will operate switch S1 and then shuffle the thumbwheel switches TWS1 through TWS8 such that none of the switches produces a correct code. Once the code does not match, pressing of switch S1 has no effect on the output of the flip-flop.Switches TWS9 through TWS16 are concealed after setting the desired code. In place of thumbwheel switches TWS1 through TWS8 DIP switches can also be used
Programmable Digital Code Lock
With the code set correctly, the NAND gate output will stay low and flip-flop can be toggled any number of times, making it possible to switch on or switch off the relay, as desired. Suppose we are using the system for switching-on of a deck for which the power supply is routed via the contacts of the relay. The authorised person would select correct code which would cause the supply to become available to the deck. After use he will operate switch S1 and then shuffle the thumbwheel switches TWS1 through TWS8 such that none of the switches produces a correct code. Once the code does not match, pressing of switch S1 has no effect on the output of the flip-flop.Switches TWS9 through TWS16 are concealed after setting the desired code. In place of thumbwheel switches TWS1 through TWS8 DIP switches can also be used
Ultrasonic Pest Repeller
Simple IF Signal Generator
The oscillator section may be easily modified for any other intermediate frequency by using ceramic filter or resonator of that frequency and by making appropriate changes in the tank circuit at collector of transistor T3. Slight adjustment of bias can be affected by varying values of resistors R6 and R7, if required
TV remote control Blocker

Just point this small device at the TV and the remote gets jammed . The circuit is self explanatory . 555 is wired as an astable multivibrator for a frequency of nearly 38 kHz. This is the frequency at which most of the modern TVs receive the IR beam . The transistor acts as a current source supplying roughly 25mA to the infra red LEDs. To increase the range of the circuit simply decrease the value of the 180 ohm resistor to not less than 100 ohm.
It is required to adjust the 10K potentiometer while pointing the device at your TV to block the IR rays from the remote. This can be done by trial and error until the remote no longer responds.
Flashy Christmas Lights

JAM (Just A Minute) Circuit

Electronic Scoring Game



You can play this game alone or with your friends. The circuit comprises a timer IC, two decade counters and a display driver along with a 7-segment display. The game is simple. As stated above, it is a scoring game and the competitor who scores 100 points rapidly (in short steps) is the winner. For scoring, one has the option of pressing either switch S2 or S3. Switch S2, when pressed, makes the counter count in the forward direction, while switch S3 helps to count downwards. Before starting a fresh game, and for that matter even a fresh move, you must press switch S1 to reset the circuit. Thereafter, press any of the two switches, i.e. S2 or S3. On pressing switch S2 or S3, the counters BCD outputs change very rapidly and when you release the switch, the last number remains latched at the output of IC2. The latched BCD number is input to BCD to 7-segment decoder/driver IC3 which drives a common-anode display DIS1. However, you can read this number only when you press switch S4. The sequence of operations for playing the game between, say two players X and Y, is summarised below:
1. Player X starts by momentary pressing of reset switch S1 followed by pressing and releasing of either switch S2 or S3. Thereafter he presses switch S4 to read the display (score) and notes down this number (say X1) manually.
2. Player Y also starts by momentary pressing of switch S1 followed by pressing of switch S2 or S3 and then notes down his score (say Y1), after pressing switch S4, exactly in the same fashion as done by the first player.
3. Player X again presses switch S1 and repeats the steps shown in step 1 above and notes down his new score (say, X2). He adds up this score to his previous score. The same procedure is repeated by player Y in his turn.
4. The game carries on until the score attained by one of the two players totals up to or exceeds 100, to be declared as the winner.
Several players can participate in this game, with each getting a chance to score during his own turn. The assembly can be done using a multipurpose board. Fix the display (LEDs and 7-segment display) on top of the cabinet along with the three switches. The supply voltage for the circuit is 5V
 |